Similar
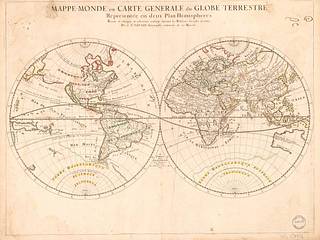
Mappe-monde, ou carte generale du globe terrestre : representée en deux plan-hemispheres : reveiie et changée en plusieurs endroits suivant les relations les plus recentes
Summary
Relief shown pictorially.
Shows California as an island.
LC copy: left half mounted on paper, fold lined. Lightly hand colored to mark continental boundaries and some place names.
Shirley, Rodney W. Mapping of the world. 1983, 419
Available also through the Library of Congress Web site as a raster image.
In the 17th century, maps took a huge leap forward. Mathematical and astronomical knowledge necessary to make accurate measurements had evolved. English mathematicians had perfected triangulation: navigation and surveying by right-angled triangles. Triangulation allowed navigators to set accurate courses and produced accurate land surveys. Seamen learned to correct their compasses for declination and had determined the existence of annual compass variation. Latitude determination was greatly improved with the John Davis quadrant. The measurement of distance sailed at sea was improved by another English invention, the common log. Longitudinal distance between Europe and Québec was determined by solar and lunar eclipses by the Jesuit Bressani in the 1640s and by Jean Deshayes in 1686. With accurate surveys in Europe, the grid of the modern map began to take shape.
Tags
Date
Location
Source
Copyright info
























