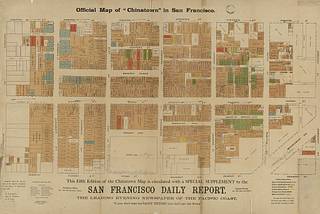
Official map of "Chinatown" in San Francisco /
Summary
Cadastral map showing names of owners, businesses, "Chinese occupancy," "Chinese gambling houses," and "White occupants."
"The map and colors show only the first, or street floor of Chinatown and the occupancy of same."
LC copy annotated in pencil
Available also through the Library of Congress Web site as a raster image.
Includes note and list of names of Mayor and Supervisors.
In the 19th century, a majority of Chinese immigrants were single men who worked for a while and returned home. At first, they were attracted to North America by the gold rush in California. A relatively large group of Chinese immigrated to the United States between the start of the California gold rush in 1849 and 1882, before federal law stopped their immigration. After the gold rush, Chinese immigrants worked as agricultural laborers, on railroad construction crews throughout the West, and in low-paying industrial jobs. Soon, many opened their own businesses such as restaurants, laundries, and other personal service concerns. With the onset of hard economic times in the 1870s, European immigrants and Americans began to compete for the jobs traditionally reserved for the Chinese. Such competition was accompanied by anti-Chinese sentiment, riots, and pressure, especially in California, for the exclusion of Chinese immigrants from the United States. The result was the Chinese Exclusion Act, passed by Congress in 1882. This Act virtually ended Chinese immigration for nearly a century.
Tags
Date
Contributors
Source
Copyright info

































